Crypto Tax in India: Everything you need to know
- by B2B Desk 2024-06-27 11:29:38
In India, profits from virtual digital assets like cryptocurrencies and NFTs are subject to a fixed 30% tax rate, as well as a 1% Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) for transactions above certain thresholds. Discover the different kinds of crypto taxes in India, covering the tax implications and percentages for actions like trading, mining, receiving cryptocurrencies as gifts, staking, and others.
Navigating the dynamic landscape of cryptocurrencies in India involves understanding the regulatory framework and implications of crypto tax in India. The cryptocurrency market in India is thriving, with a notable increase in adoption rates and market growth expected to remain strong in the near future. The Indian government has acknowledged the potential and has moved from being cautious to implementing proactive regulation and taxation to maintain financial stability and prevent tax evasion.
Crypto Tax in India- Explained
As of April 1, 2022, cryptocurrencies are now taxed under a new system as Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs), reflecting their growing acceptance in everyday life. Investors and traders need to grasp these regulations to manage their portfolios effectively and comply with legal requirements.
Here's how the new tax on income from Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) operates
Assets Subject to the New Tax
Changes to the Income Tax Act as of April 1, 2022 now include provisions for taxing profits and earnings from VDAs. According to the Income Tax Act, VDAs refer to:
- Cryptocurrencies are neither considered Indian nor foreign currency under the Income Tax Act, with the proposed digital Rupee potentially being an exception. The Act defines cryptocurrencies as information, code, number, or token generated through cryptographic means, representing value exchanged with or without consideration, promising inherent value, functioning as a store of value or unit of account, and being used in financial transactions or investments, including schemes, and can be electronically transferred, stored, or traded.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) or similar tokens as notified by the Central Government.; and
- Other digital assets as specified by the Central Government.
Interestingly, neither blockchain nor DLT are mentioned in the VDAs definition in the Income Tax Act.
The Central Government has not yet informed which NFTs, tokens, or other VDAs will be subject to the provisions of the Income Tax Act. It could be argued that currently no NFTs are included in the new tax rules, but tax authorities may choose to tax NFTs as part of cryptocurrency due to the broad definition that includes tokens. Taxpayers should consider that NFTs they buy, sell, or handle in any way are probably subject to taxation.
Understanding the concept of Crypto Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
The Financial Budget 2022 introduced Tax Deductible at Source (TDS) along with 30% crypto tax in India.
TDS plans to levy fees on cryptocurrency investors and traders directly for all their transactions. When TDS is deducted, the deductor must withhold the TDS amount from the total payment and send it to the central government if they owe a specific amount to the deductee.
In India, 1% is deducted as TDS on crypto amounts.
Starting July 1, 2022, buyers will deduct a 1% TDS when paying sellers for Crypto/NFT transfers. If the transaction happens on an exchange, the exchange may deduct this TDS and then pay the seller the remaining balance.
Indian exchanges will deduct the TDS automatically.
Nonetheless, individuals who engage in trading on international stock markets are required to deduct TDS themselves and submit their TDS returns.
The taxation of cryptocurrency in India could be flexible as it may vary in the future. Nevertheless, we can now grasp the consequences of this 1% TDS and its impact on you and your cryptocurrency transactions.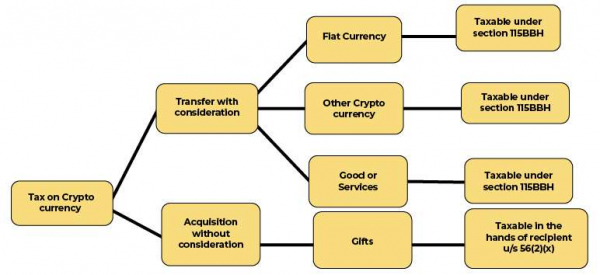
Is it possible to evade taxes on cryptocurrencies in India?
It's crucial to note that attempting to evade crypto tax in India is illegal and poses substantial risks.
Major trading platforms such as WazirX gather customer data and must comply with IRS reporting requirements when asked.
Lately, the Indian government has shown a keen interest in the crypto ecosystem. In the year 2022, the IRS confiscated over 95 crore INR from 11 crypto exchanges alleged to have committed tax evasion.
How can I reduce my tax liability on cryptocurrencies in India?
Even though it is impossible to evade the 30% tax legally, techniques such as purchasing and keeping your cryptocurrency for an extended period can assist in reducing your tax obligation and taking advantage of your coins' continuous increase in value.
What steps should investors take?
Indian laws regarding voluntary disclosure agreements (VDAs) are continuously developing. Even though the Government has announced the new tax system, it is expected that the system will be revised in the future.
- Currently, individuals planning to invest or trade in VDAs should understand the new tax rules and seek advice from a tax advisor before getting started. It's advisable to conduct VDA transactions on exchanges or marketplaces rather than through off-market dealings. This approach can help establish the fair market value of VDAs, especially in the absence of clear government guidance.
- Taxpayers should be aware that they cannot offset losses from one source against gains from another. Furthermore, expenses related to activities like cryptocurrency mining or NFT minting cannot be deducted from profits earned on VDAs.
- Individuals interested in acquiring or trading NFTs should stay informed and monitor government updates to determine if these specific NFTs are classified as Virtual Digital Assets (VDAs) under the Income Tax Act.
FAQs
Q. Is crypto income taxable in India?
A. Yes, cryptocurrency is liable to tax in India. In the 2022 budget, new rules related to the taxation of cryptocurrencies have been introduced. It was kept at a flat 30% on income from the transfer of digital assets such as cryptocurrencies.
Q. Is crypto legal in India?
A. Cryptocurrency trading and investment are legal in India, but the regulatory framework is still evolving. In 2018, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) issued a circular that prohibited banks and other regulated entities from providing services to businesses dealing with virtual currencies.
Q. Is Binance P2P trading legal in India?
A. Currently banned by the Indian government, crypto exchange Binance has discontinued the cash payment option for peer to peer (P2P) trades conducted in rupees
Q. How can I avoid 30% crypto tax in India?
A. Selling: You may be liable for a 30% tax on any profits if you plan on selling, swapping, or spending the received tokens later. Buying: Earning new tokens is taxed upon receipt at your Individual Tax Rate. Since no buying or selling is taking place while holding onto your crypto assets, there is no tax on the same.
Q. What is the TDS for crypto?
A. There's a 30% tax on cryptocurrency earnings and a 1% TDS deducted at source implemented in the 2022 Union Budget. The 1% TDS on crypto transfers aims to track transaction information. TDS in crypto transactions includes various scenarios and must be paid to the Central Government.
Also Read: What Is an Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF)? A Complete GuidePOPULAR POSTS
How India’s Online Gaming Ban Triggered a 25% Drop in UPI Payments in Just 9 Days
by Shan, 2025-09-09 12:13:47
Cryptocurrency Explained: How It Works, Key Types, Benefits & Real-World Risks
by Shan, 2025-07-23 08:28:31
Trump’s Big Beautiful Bill Sparks Crypto Clash in Senate: What’s at Stake for Investors?
by Shan, 2025-07-01 12:24:17
$90 Million Crypto Hack at Iran’s Nobitex: Israel-Linked Group Claims Responsibility
by Shan, 2025-06-26 09:43:52
JioCoin: What Is It and How to Earn It Effortlessly?
by B2B Desk, 2025-01-22 09:05:13
Bitcoin Crosses USD 101,000 Amid Optimism Over US Inflation Data Likely Pushing a Fed Rate Cut Decision
by B2B Desk, 2024-12-12 09:49:25
Bitcoin Hits New All-Time High Above USD 100,000 on Optimism Over Donald Trump’s Crypto Plans
by B2B Desk, 2024-12-05 06:20:24
RECENTLY PUBLISHED

How a Free AI Visibility Tool Helps Businesses Grow in the AI Driven Search Era
- by Aakash Ladha , 2026-03-06 10:40:04

Loan EMIs to Drop as RBI Slashes Repo Rate - Full MPC December 2025 Highlights
- by Shan, 2025-12-05 11:49:44

The Agentic Revolution: Why Salesforce Is Betting Its Future on AI Agents
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 10:29:23

Pine Labs IPO 2025: Listing Date, Grey Market Premium, and Expert Outlook
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 09:57:07

Top 10 Insurance Companies in India 2026: Life, Health, and General Insurance Leaders Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-30 10:06:42

OpenAI Offers ChatGPT Go Free in India: What’s Behind This Big AI Giveaway?
- by Shan, 2025-10-28 12:19:11




 Subscribe now
Subscribe now 