What is the Difference Between FERA and FEMA?
- by B2B Desk 2024-05-31 10:20:23
Differentiating between FERA and FEMA is crucial for individuals interested in international business, finance, or law in India. FERA (Foreign Exchange Regulation Act) and FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act) are both vital laws governing foreign exchange. They profoundly influence investment and business in India, yet operate on distinct principles and platforms, reflecting the economic and social demands of their respective periods.
What is FERA?
The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act, commonly known as FERA, was enacted in 1973. The Act was enacted to regulate foreign exchange rates, securities, importation of currency and including export and purchase of securities by foreigners. The Act was promulgated in India when the situation in other countries was unsatisfactory. It aims to conserve foreign currency and its best use in economic development.
The work affects the entire country. Therefore, all citizens of the country, whether inside or outside India are covered under this Act. The act covers branches and offices of Indian multinationals operating outside the country, owned and managed by a resident of India.
What is FEMA?
FEMA expands the Foreign Exchange Management Act of 1999, repealing and replacing previous laws. The Act applies to all branches and agencies of the entity operating throughout India and outside India. The owners or managers of this company are residents of India and this Act also applies to any offense committed outside India by a person subject to this Act.
The main purpose of the law is to promote foreign trade and encourage the systematic development and maintenance of the domestic foreign exchange market. This law consists of a total of 7 chapters. Of the 49 articles, 12 articles deal with the operational part and the remaining 37 articles deal with punishments, violations, appeals, judgments, etc.
Difference Between FERA and FEMA
Below are the key points that highlight the differences between FERA and FEMA-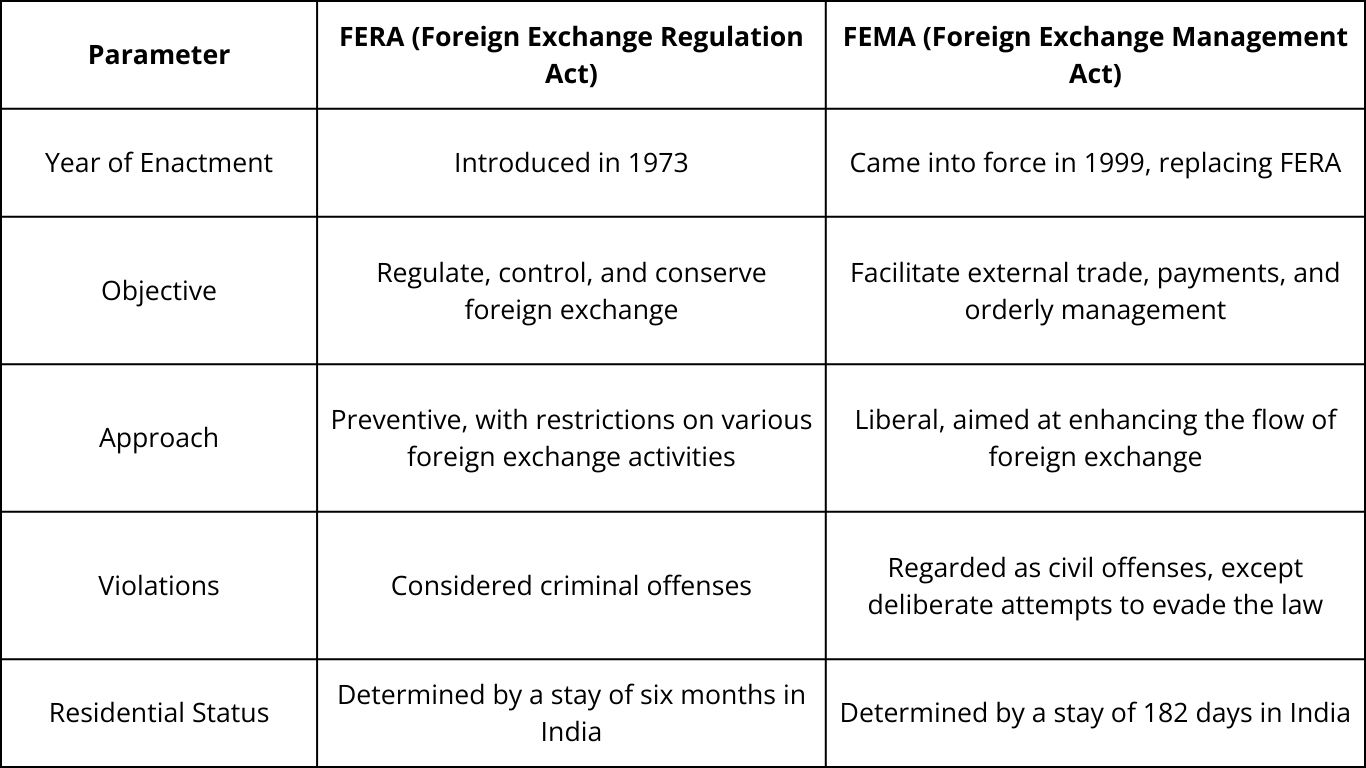
Similarities Between FERA and FEMA
Although FERA has been replaced by FEMA, they both have the same similarities.
- FERA and FEMA were implemented to oversee and control the foreign exchange market in India.
- Both laws are implemented by the Reserve Bank of India.
- Both FERA and FEMA contain provisions for penalizing individuals and entities who breach the regulations.
- FERA and FEMA aim to safeguard foreign exchange reserves and ensure their appropriate utilization.
Under these acts, the Central Government holds the authority to impose restrictions on specific types of foreign exchange activities. However, the key difference between FERA and FEMA lies in their regulatory approach and scope of application.
Bottom line
FERA and FEMA can be said to be the two laws of India which control the foreign money transactions in India. While FERA and FEMA are closely related, they differ in key areas. FERA is a provincial law while FEMA is an open law. While FERA introduced strict regulations, FEMA gave international companies more flexibility. FERA was created primarily to control foreign exchange transactions while FEMA was created to streamline and liberalize the rules governing such transactions. The key difference between FERA and FEMA lies in their regulatory approach and scope of application.
FAQs
Q. Is FEMA replaced by Fera?
A. The act came into force on 1st January 1974. The FEMA Act was passed by the Parliament of India in 1999 to replace the FERA. It came into force on 1st June 2000. The FERA Act was repealed by the Vajpayee government in 1998.
Q. What was the main objective of Fera?
A. FERA was replaced by FEMA. FERA or the Foreign Exchange Regulation Act was introduced in the year 1973 at a time when the foreign reserves of the country were quite low. Its main purpose was to regulate the foreign exchanges so as to maintain a satisfactory account of the foreign reserves in the country.
Q. What is the full form of Fera in India?
A. The Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) was legislation passed in India in 1973 that imposed strict regulations on certain kinds of payments, the dealings in foreign exchange (forex) and securities and the transactions which had an indirect impact on the foreign exchange and the import and export of currency.
Q. When was FEMA executed?
A. The Foreign Exchange Management Act, 1999 (FEMA) deals with cross border investments, foreign exchange transactions and transactions between residents and non-residents. It has come into force from June 1, 2000. The operation of FEMA is akin to any other commercial law.
Also Read: NSE Indices Introduces India's First EV Index: Here's what you should know
POPULAR POSTS
How a Free AI Visibility Tool Helps Businesses Grow in the AI Driven Search Era
by Aakash Ladha , 2026-03-06 10:40:04
Loan EMIs to Drop as RBI Slashes Repo Rate - Full MPC December 2025 Highlights
by Shan, 2025-12-05 11:49:44
Zoho Mail vs Gmail (2025): Which Email Platform Is Best for Businesses, Startups, and Students?
by Shan, 2025-10-09 12:17:26
PM Modi Launches GST Bachat Utsav: Lower Taxes, More Savings for Every Indian Household
by Shan, 2025-09-24 12:20:59
$100K H-1B Visa Fee Explained: Trump’s New Rule, Clarifications & Impact on Indian Tech Workers
by Shan, 2025-09-22 10:11:03
India-US Trade Deal Soon? Chief US Negotiator Arrives in Delhi as Talks Set to Begin Tomorrow
by Shan, 2025-09-15 11:54:28
Modi Meets Xi: Trump’s Tariffs, Strategic Autonomy, and the Future of Asia’s Power Balance
by Shan, 2025-09-03 06:40:06
RECENTLY PUBLISHED

Pine Labs IPO 2025: Listing Date, Grey Market Premium, and Expert Outlook
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 09:57:07

The Agentic Revolution: Why Salesforce Is Betting Its Future on AI Agents
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 10:29:23

Top 10 Insurance Companies in India 2026: Life, Health, and General Insurance Leaders Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-30 10:06:42

OpenAI Offers ChatGPT Go Free in India: What’s Behind This Big AI Giveaway?
- by Shan, 2025-10-28 12:19:11

Best Silver Investment Platforms for 2025: From CFDs to Digital Vaults Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-23 12:22:46





 Subscribe now
Subscribe now 