What is the Difference between tax evasion and tax avoidance
- by B2B Desk 2024-05-27 08:24:24
The legal aspect is what distinguishes tax evasion from tax avoidance. People who have the necessary funds and resources are able to decrease the amount of taxes they owe by using different tax laws, deductions, and methods within the confines of the law. They utilize legal means to reduce their tax liability, which is known as tax avoidance. Alternatively, tax evasion consists of unlawful actions like falsely declaring income or hiding assets to evade tax obligations. In this article, you will discover the distinction between tax avoidance and tax evasion and the reasons why attempting to evade tax payments is not advisable.
What is Tax Evasion?
Tax evasion is the illegal act of intentionally evading taxes by deceptive or fraudulent means. It is defined as intentional non-compliance with tax regulations, which can include actions such as concealing income, maintaining unreported offshore accounts, falsifying documents, or engaging in other fraudulent activities. For example, claiming depreciation on assets used for home use or claiming depreciation on assets not used in a business.
Examples of tax evasion
- Providing inaccurate information about one's income, assets, or profits constitutes a false declaration.
- Fabricating records.
- Not paying enough taxes
- Intentionally concealing business transactions from records.
- Overstating expenses, etc.
What is Tax Avoidance?
Tax evasion is a legal method used to avoid the intended purpose of a law by exploiting loopholes in the tax code. It involves developing creative ways or means to avoid taxes while staying within the bounds of the law.
This can be achieved by changing the financial records in a way that does not conflict with the tax rules and also reduce the tax collected. Tax evasion was once considered a crime, but is now classified as a crime under certain circumstances.
Tax avoidance only reduces, delays and sometimes eliminates the tax burden. This can be achieved by participating in government programs and incentives such as exemptions, rebates, tax benefits, tax credits and other subsidies that reduce tax liabilities. without breaking the law or committing a crime.
Examples of tax avoidance
- Increase in cost to earn revenue.
- Increase in the number of children.
- Transfer your assets to your children to evade inheritance tax.
- Putting money into a retirement fund.
- Give charity to claim deductions, etc.
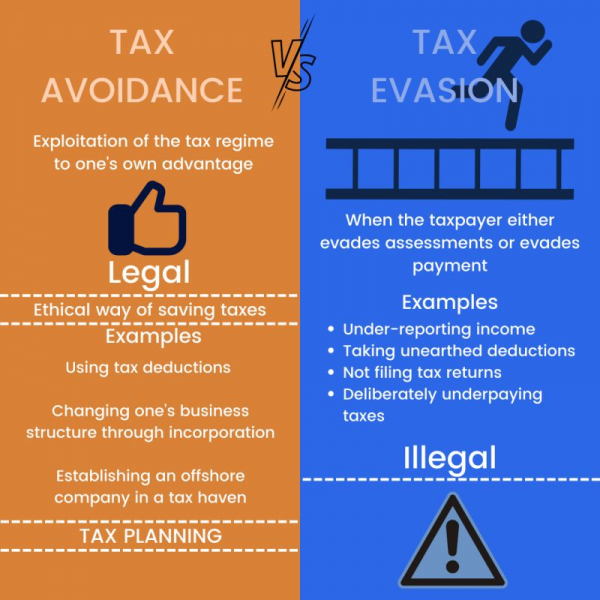
Differences Between Tax Evasion and Tax Avoidance
Although tax evasion and tax avoidance involve efforts to reduce tax payments, they stand on opposite sides of the legal spectrum. Here are the main differences:
Legality: Tax evasion is against the law and includes intentional dishonesty to trick tax authorities, whereas tax avoidance follows the rules and uses acceptable ways to lower tax obligations.
Transparency: Tax avoidance usually involves the transparent utilization of legal tax reliefs and allowances. On the other hand, tax evasion is not transparent and includes deceitful methods such as lowering reported earnings or altering documents.
Penalties: Tax evasion may result in serious consequences such as jail time and large fines due to its unlawful nature. On the other hand, tax avoidance does not result in penalties, but authorities might question avoidance schemes that are too aggressive.
Ethics: Tax avoidance is often seen as a smart financial strategy, although it can raise practical questions if it's more complicated. Tax returns are not accepted because they are fraudulent.
Impact on Public Finance: Although tax avoidance is within the bounds of the law, it can still have a negative impact on public finances when used excessively by those with high incomes or corporations, as it shrinks the tax revenue necessary to support public services.
In conclusion, tax evasion and tax avoidance are frequently used interchangeably, despite actually representing two distinct ideas. Tax evasion is against the law and entails purposely deceiving to escape taxes, whereas tax avoidance is a lawful method to decrease tax responsibilities using legal tax planning approaches. It is important for taxpayers to comprehend the distinction in order to prevent legal problems and adhere to tax regulations.
FAQs
Q. What is tax evasion with an example?
A. It is essentially the criminal act of a person or a company attempting to avoid paying their tax obligations. It includes concealing or fabricating income and falsifying deductions without proof. Another tax evasion example is failing to declare cash transactions, etc.
Q. What is the most famous tax evasion case?
A. Al Capone. Al Capone is likely the most notorious tax evader in history. Although well-known as the king of Chicago gangsters, the federal government couldn't put together any criminal charges that would stick until they nailed Capone for failing to pay taxes.
Q.What do you mean by VAT?
A. VAT or Value Added Tax is a type of tax that is charged by the Central Government on the sale of services and goods to the consumers. VAT is paid by the producers of services and goods, but it is finally imposed on the consumers who purchase the services and goods when they pay for it.
Q. What is the most common form of tax evasion?
A. A person typically commits tax evasion when they: Do not submit a tax return when they know they should. Artificially reducing or omitting Income. Include false personal deductions on the tax return.
Also Read: SEBI's New Market Rumor Guidelines Aid Fair M&A Pricing: Experts

POPULAR POSTS
How a Free AI Visibility Tool Helps Businesses Grow in the AI Driven Search Era
by Aakash Ladha , 2026-03-06 10:40:04
Loan EMIs to Drop as RBI Slashes Repo Rate - Full MPC December 2025 Highlights
by Shan, 2025-12-05 11:49:44
Zoho Mail vs Gmail (2025): Which Email Platform Is Best for Businesses, Startups, and Students?
by Shan, 2025-10-09 12:17:26
PM Modi Launches GST Bachat Utsav: Lower Taxes, More Savings for Every Indian Household
by Shan, 2025-09-24 12:20:59
$100K H-1B Visa Fee Explained: Trump’s New Rule, Clarifications & Impact on Indian Tech Workers
by Shan, 2025-09-22 10:11:03
India-US Trade Deal Soon? Chief US Negotiator Arrives in Delhi as Talks Set to Begin Tomorrow
by Shan, 2025-09-15 11:54:28
Modi Meets Xi: Trump’s Tariffs, Strategic Autonomy, and the Future of Asia’s Power Balance
by Shan, 2025-09-03 06:40:06
RECENTLY PUBLISHED

Pine Labs IPO 2025: Listing Date, Grey Market Premium, and Expert Outlook
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 09:57:07

The Agentic Revolution: Why Salesforce Is Betting Its Future on AI Agents
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 10:29:23

Top 10 Insurance Companies in India 2026: Life, Health, and General Insurance Leaders Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-30 10:06:42

OpenAI Offers ChatGPT Go Free in India: What’s Behind This Big AI Giveaway?
- by Shan, 2025-10-28 12:19:11

Best Silver Investment Platforms for 2025: From CFDs to Digital Vaults Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-23 12:22:46





 Subscribe now
Subscribe now 