Different types of companies in India: You must know
- by B2B Desk 2024-07-01 11:46:30
The Companies Act of 2013 categorizes companies based on their membership size. Similarly, the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) Act classifies them as micro, small, and medium enterprises to provide MSME benefits. Companies can also be classified according to the liability of their members, ownership structure, and whether they are listed or not. Here are the different types of companies in India based on these criteria:
Public Limited Company
Shares of the company in this organization are owned by the general Indian public, allowing them to trade easily on the stock exchange market. While there is no restriction regarding the quantity of shareholders, a minimum of 7 individuals need to be present in order to form these types of companies in India.
Private Limited Company
In India, a private limited company is a business owned privately that has limited liability. This company can have up to 200 shareholders at maximum. The company's shares are not available for public trading or transfer, distinguishing it among types of companies in India.
Section 8 Company
A Section 8 Company is a non-profit organization that is registered for benevolent reasons, like advancing science, education, religion, art, social welfare, or any other beneficial cause.
Holding Company
A holding company is a business entity that possesses ownership of one or multiple other businesses. It's similar to a mother company, with the businesses it holds being referred to as subordinate companies. The holding company either holds over 50% of another company's shares or has control of its board of directors, either through direct ownership or through another entity. This classification is significant in understanding types of companies in India.
Unlimited Company
An unlimited company is a business structure where each member bears unlimited liability for its debts. This means that the personal assets of the members can be used to settle any obligations of the company. At any point, such a company can choose to re-register as a limited company under Section 32 of the Companies Act, highlighting its classification among types of companies in India.
Joint Hindu Family
Joint Hindu Family is a form of business organization where members of a family have ownership and management control over the business. Hindu Law is in charge of its administration.
One Person Company
A newly established form of company is known as One Person Company (OPC). OPC was included in the Companies Act 2013 to assist solo entrepreneurs in establishing a business by enabling them to form a solo economic entity. An OPC's major benefit is that it can have only one member, while a Private Limited Company or a Limited Liability Partnership needs at least two members for incorporation and maintenance. Just like a corporation, a One Person Company (OPC) is a distinct legal entity from its owners, provides limited liability to its members, ensures business continuity, and has a straightforward incorporation process. This makes OPCs a significant category among types of companies in India.
Listed Companies
Companies that have their shares listed and traded on a recognized stock exchange, like the Bombay Stock Exchange (BSE) or the National Stock Exchange (NSE) in India, are known as listed companies.
These companies must adhere to strict regulatory requirements and disclosure norms as mandated by SEBI in India. Listing allows shareholders to easily sell their shares and allows the company to raise funds by issuing more shares to the public. highlighting their categorization among types of companies in India.
Unlisted Companies
Unlisted firms are those that do not have their shares listed on any stock market. These companies might be privately owned, with their shares held by a limited number of shareholders or closely held by promoters and investors.
Unlisted companies, although not under the same level of regulatory scrutiny as listed companies, may still need to adhere to specific statutory requirements outlined in the Companies Act, distinguishing their classification among types of companies in India.
Associate Company
A partner company is a company in which another company has a substantial but not controlling stake, typically ranging from 20% to 50% of the voting rights. Although the investing company has some control over the operations and management of the associate company, it does not have complete authority.
Foreign company
A foreign subsidiary is a company where more than 50% of its shares are owned by another company incorporated in a different foreign country, known as the holding or parent company. In India, for a company to be classified as a foreign affiliate, it must be incorporated within India itself.
The location where the parent company is incorporated does not affect compliance requirements, which vary depending on factors such as the type of company, sector of operation, annual turnover, and number of employees. Additionally, foreign companies are subject to higher income tax rates ranging from 40% to 50%, exclusive of additional charges like cess and surcharge.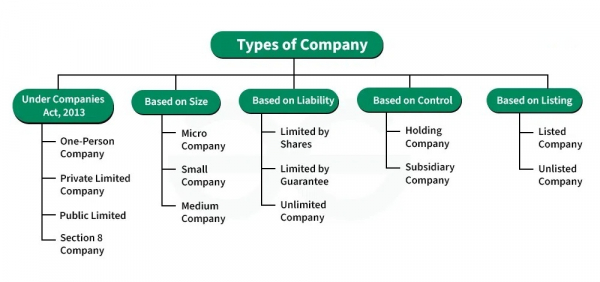
FAQs
Q. What are the classification of company?
A. Companies can be classified as Private Limited Companies, Public Limited Companies, or One Person Companies. Each classification has its own set of rules governing ownership, shareholder rights, and decision-making processes.
Q. Which is the No 1 company in India?
A. Reliance Industries, a conglomerate holding company, is the largest company in India by market cap. It operates in various sectors, including energy, petrochemicals, textiles, natural resources, retail, and telecommunications.
Q. What is the difference between LLP and Pvt Ltd?
A. The partners are the LLP owners and manage the LLP business. A partner in an LLP is a manager and an owner, while in a Pvt Ltd company, the owners, i.e. shareholders, do not have managerial powers. In a Pvt Ltd company, the management is different from the owners. The board of directors manage the company business.
Q. In which sector is India no 1?
A. India is the world's largest producer of milk, pulses and jute, and ranks as the second largest producer of rice, wheat, sugarcane, groundnut, vegetables, fruit and cotton.
Q. How many types of companies are there in India?
A. There are 7 types of entities recognized under the Indian Law namely Private Limited Company, Public Company, Sole Proprietorship, One Person Company, Partnership, Limited Liability Partnership (LLP). The type of entities are described in detail below.
Also Read: Rapido Business Model: How Rapido Generates Revenue?
POPULAR POSTS
How a Free AI Visibility Tool Helps Businesses Grow in the AI Driven Search Era
by Aakash Ladha , 2026-03-06 10:40:04
Loan EMIs to Drop as RBI Slashes Repo Rate - Full MPC December 2025 Highlights
by Shan, 2025-12-05 11:49:44
Zoho Mail vs Gmail (2025): Which Email Platform Is Best for Businesses, Startups, and Students?
by Shan, 2025-10-09 12:17:26
PM Modi Launches GST Bachat Utsav: Lower Taxes, More Savings for Every Indian Household
by Shan, 2025-09-24 12:20:59
$100K H-1B Visa Fee Explained: Trump’s New Rule, Clarifications & Impact on Indian Tech Workers
by Shan, 2025-09-22 10:11:03
India-US Trade Deal Soon? Chief US Negotiator Arrives in Delhi as Talks Set to Begin Tomorrow
by Shan, 2025-09-15 11:54:28
Modi Meets Xi: Trump’s Tariffs, Strategic Autonomy, and the Future of Asia’s Power Balance
by Shan, 2025-09-03 06:40:06
RECENTLY PUBLISHED

Pine Labs IPO 2025: Listing Date, Grey Market Premium, and Expert Outlook
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 09:57:07

The Agentic Revolution: Why Salesforce Is Betting Its Future on AI Agents
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 10:29:23

Top 10 Insurance Companies in India 2026: Life, Health, and General Insurance Leaders Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-30 10:06:42

OpenAI Offers ChatGPT Go Free in India: What’s Behind This Big AI Giveaway?
- by Shan, 2025-10-28 12:19:11

Best Silver Investment Platforms for 2025: From CFDs to Digital Vaults Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-23 12:22:46





 Subscribe now
Subscribe now 