What is NSC - National Savings Certificate? Know it all here!
Who can Invest in NSC? A National Savings Certificate can be purchased by anybody over the age of ten, as well as legal guardians or parents acting on behalf
- by B2B Desk 2022-04-29 07:05:21
When it comes to investments, there are numerous alternatives. You can select any of them based on your financial objectives. The National Savings Certificate, or NSC, is a popular post office savings product. It offers a slew of advantages as a low-risk investment.
What is National Savings Certificate?
The National Savings Certificate (NSC) is a fixed-income investment option available at any post office branch. The plan is an initiative of the Indian government. It's a savings bond that encourages subscribers – mostly low- to mid-income investors – to save while reducing their tax liability.
This fixed-income product, like the Public Provident Fund and Post Office FDs, is a low-risk fixed-income vehicle. You can get it in your yourself, for a juvenile, or as a joint account with another adult at your local post office. The maturity time for NSC is set at five years. The purchase of NSCs has no upper limit, but only investments of up to Rs.1.5 lakh qualify for a tax credit under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. The certificates earn a fixed rate of interest, which is presently 6.8% per year. The government adjusts the interest rate on a regular basis.
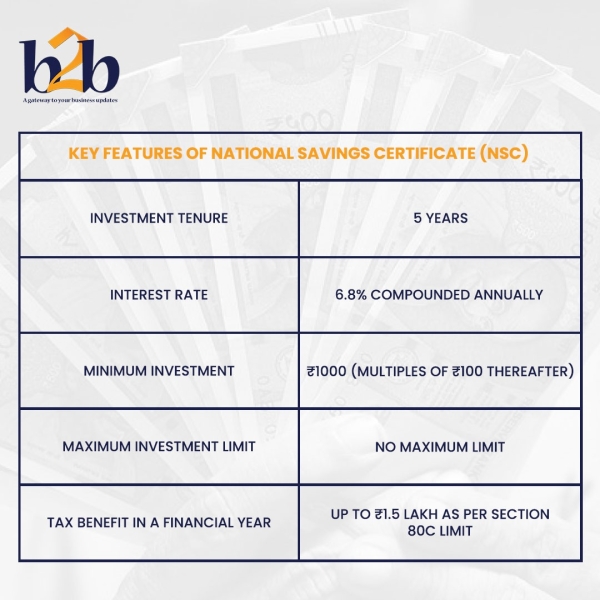
Who can Invest in NSC?
A National Savings Certificate can be purchased by anybody over the age of ten, as well as legal guardians or parents acting on behalf of a minor. In NSC, one can earn guaranteed returns at the current interest rate. Anyone looking for a safe way to make a consistent return while avoiding taxes might consider investing in NSC. NSC provides interest guarantees as well as comprehensive capital protection. However, unlike tax-saving mutual funds and the National Pension System, they are unable to generate inflation-beating returns. The government has made NSC widely available to potential investors by placing it at post office offices across the country.
Individuals can save via the National Savings Certificate, which is supported by the government. As a result, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs) and trusts are unable to invest. NSC certifications are also unavailable to non-resident Indians (NRIs). The scheme is exclusively available to Indian people who live in India.
How and where can you buy NSC?
The National Savings Certificate is currently available in two formats: electronic mode (e-mode) and Passbook mode. They are available for purchase at public sector banks, select authorised private banks, and post offices.
If your Internet Banking is operational, you can acquire the National Savings Certificate online in e-mode if you have a savings account at an authorised bank or post office. The NSC interest rate is currently 6.8% compounded annually. Please note that in July 2016, the physically pre-printed National Savings Certificates issued by post offices and banks were phased out.
What is the NSC certificate number?
Every NSC certificate has a unique certificate number that includes important information such as the post office branch that issued the certificate. The NSC Certificate Number is clearly visible on the certificate and can be used to verify the NSC investment's legitimacy and authenticity.
Tax benefits of NSC.
NSC's principal tax benefit is provided by Section 80C of the Internal Revenue Code. This enables investors to claim a tax deduction of up to 1.5 lakh in a single financial year under section 80C. However, other tax-saving investments, like as PPF, EPF, and ELSS Mutual Funds, as well as life insurance premium payments, are included in the 1.5 lakh limit.
On NSC interest collected during the first four years of the investment, a supplementary tax deduction is available. This is due to the fact that NSC's interest is re-invested for the next four years. The interest earned on NSC in the fifth year, i.e., at maturity, is taxed at the slab rate under the heading "Income from Other Sources."
Let's look at an example to help us comprehend. Assume you've invested $5,000 in National Savings Certificates. Section 80C now allows you to deduct the original investment amount in the first year. The interest of 340 generated in the first year will appear under the heading Income from Other Sources in the second year. This amount, on the other hand, can be claimed as a deduction under Section 80C. Similarly, you can claim an annual deduction u/s 80C on the interest generated from an NSC until it matures. The amount of interest paid out at maturity will be taxed at your marginal tax rate.
NSC's Features and Benefits
The following are some of the most important features and benefits of National Savings Certificates:
- Fixed Income: You may expect consistent and predictable returns. The current interest rate on the National Savings Certificate is 6.8% per year. Furthermore, the government changes the rates every quarter. By investing in National Savings Certificates for 5 to 10 years, you can be certain of a positive return.
- Interest compounding: For the first four years, interest collected on the investment is compounded annually and reinvested. For the first four years, you can deduct your expenses. NSC interest is taxable because it is not reinvested in the previous year.
- Nomination facility: The investor has the option of nominating a family member or a minor. In the event of the investor's death, the maturity profits will be inherited by the nominee. The rules for nomination are as follows:
- There can only be one nominee unless the National Savings Certificate has a denomination of $500 or higher.
- The guardian or adult responsible for the minor should be reported to the bank or post office if the nominee is a minor.
- If the National Savings Certificate is held by a minor, the nomination feature is not available.
- Easy investment option: National Savings Certificates are a simple investment option that may be made at any post office or recognised public and private sector institutions. All you need to do now is provide the necessary KYC documents. The entire procedure is simple and straightforward.
- Tax benefit: Investments in National Savings Certificates are eligible for a Section 80C deduction up to a maximum of 1.5 lakhs per financial year. As a result, you can benefit from tax advantages on your investments.
- Risk is low: National Savings Certificates are considered low-risk investment alternatives because the Indian government backs them. They are perfect for risk-averse individuals.
- Facility of loan: Individuals can borrow money against their National Savings Certificates by using them as collateral with banks.
- Premature Withdrawal: Premature withdrawal from a National Savings Certificate is usually not allowed. It may, however, be permitted in certain circumstances. A court order or the death of the actual investor are examples of this.
NSC Modes and Types
The following are the many ways in which investors can own a National Savings Certificate:
Single Holder Certificate: As the name implies, single holder certificates are only granted to single people. He or she has the option of nominating someone for the certificate. The original holder, however, retains decision-making authority. Furthermore, these certificates might be provided to a minor's legal guardian.
Joint 'A' Type Certificate: Joint 'A' type certificates are given to two adults who are joint holders. The proceeds of the certificate are payable to both joint holders when it matures. Both people have equal decision-making authority. The signatures of both joint holders are required even when appointing a nominee, cancelling or transferring the nomination.
National Savings Certificate, Joint 'B' Sort: This type of National Savings Certificate is also given to two adults. The fundamental difference between type 'A' and type 'B', however, is that the latter pays the maturity value to any of the joint holders. Types 'B' and 'A' have the same decision-making and nomination rights.'
What is the NSC Maturity Period and How Can I Withdraw Early?
The NSC VIII Issue has a 5-year maturity period. Your NSC investments are locked in for the next 5 years and cannot be removed. Premature withdrawal of NSC investments is permitted only if the following conditions are met:
- All joint account holders or the only account holder have died.
- The NSC investments must be withdrawn early due to a court injunction.
- The money is given to a Gazetted Officer or another government official and then forfeited.
NSC Documents Required
The following is a list of the documents required to purchase a National Savings Certificate:
- Completed NSC Application Form
- PAN, Aadhaar Card, Driver's License, and other identity proof documents
- Documentation proving your address, such as an Aadhaar card, a passport, a phone bill, and so on.
- Photograph taken recently
- The amount you desire to invest can be paid in cash or by cheque.
How Do I Redeem My NSC Certificate When It Comes to Maturity?
In March 2016, pre-printed NSC certificates were phased out. As a result, NSC investments made after April 2016 will either be in the form of an e-NSC certificate or a real NSC Passbook.
To redeem your e-NSC certificate, connect into the same Internet Banking account that you used to obtain the NSC certificate. You can use the portal to seek the redemption of your e-NSC certificate once you've logged in. The sum will be credited to your linked savings account after the redemption is finished.
If you have a real NSC passbook, you must redeem your investment at the Post Office branch where it was issued. Along with an application for redemption of your NSC investments, you'll need to fill out a redemption request form and attach essential papers like your NSC passbook, a government-issued Identity Proof like Aadhaar or PAN, and a government-issued Identity Proof like Aadhaar or PAN. Your redemption request will be completed and the proceeds will be deposited to your bank account when you submit these documents at the Post Office.
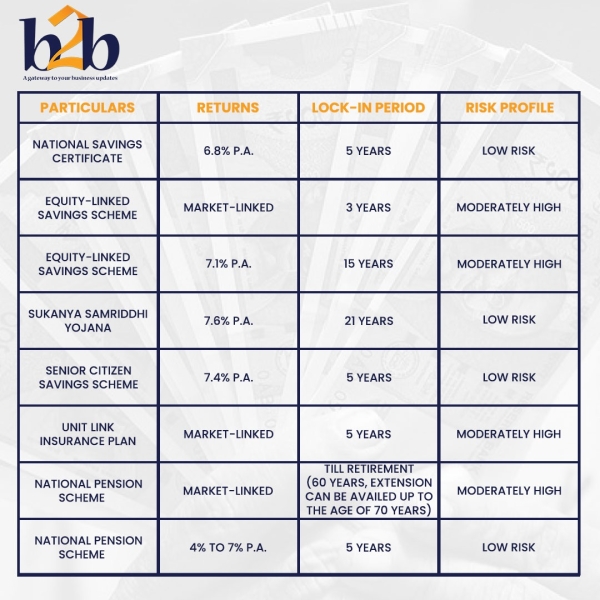
Other Tax-Saving Schemes vs. the National Savings Certificate
Also Read: Norway’s Scatec striving for hydropower assets in India
POPULAR POSTS
Best Silver Investment Platforms for 2025: From CFDs to Digital Vaults Explained
by Shan, 2025-10-23 12:22:46
Best Investment Plans in India for 2025: A Complete Guide to Grow and Protect Your Wealth
by Shan, 2025-09-18 10:20:46
Which venture capital firms are the most active in funding Indian startups in 2025
by Shan, 2025-08-06 10:42:11
Top 5 Apps to Buy Digital Gold in India (2025): Safe, Simple & Secure
by Shan, 2025-08-01 10:24:51
10 Highest Dividend Yield Stocks in August 2025
by Shan, 2025-07-28 09:31:02
Exchange-Traded Fund (ETF): A Practical Guide to Smart Investing
by Anmol Chitransh, 2025-04-17 10:18:20
The Ultimate Guide to Commodity Trading: Strategies, Risks, and Opportunities
by Anmol Chitransh, 2025-04-02 07:06:01
RECENTLY PUBLISHED

How a Free AI Visibility Tool Helps Businesses Grow in the AI Driven Search Era
- by Aakash Ladha , 2026-03-06 10:40:04

Loan EMIs to Drop as RBI Slashes Repo Rate - Full MPC December 2025 Highlights
- by Shan, 2025-12-05 11:49:44

The Agentic Revolution: Why Salesforce Is Betting Its Future on AI Agents
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 10:29:23

Pine Labs IPO 2025: Listing Date, Grey Market Premium, and Expert Outlook
- by Shan, 2025-11-05 09:57:07

Top 10 Insurance Companies in India 2026: Life, Health, and General Insurance Leaders Explained
- by Shan, 2025-10-30 10:06:42

OpenAI Offers ChatGPT Go Free in India: What’s Behind This Big AI Giveaway?
- by Shan, 2025-10-28 12:19:11




 Subscribe now
Subscribe now 